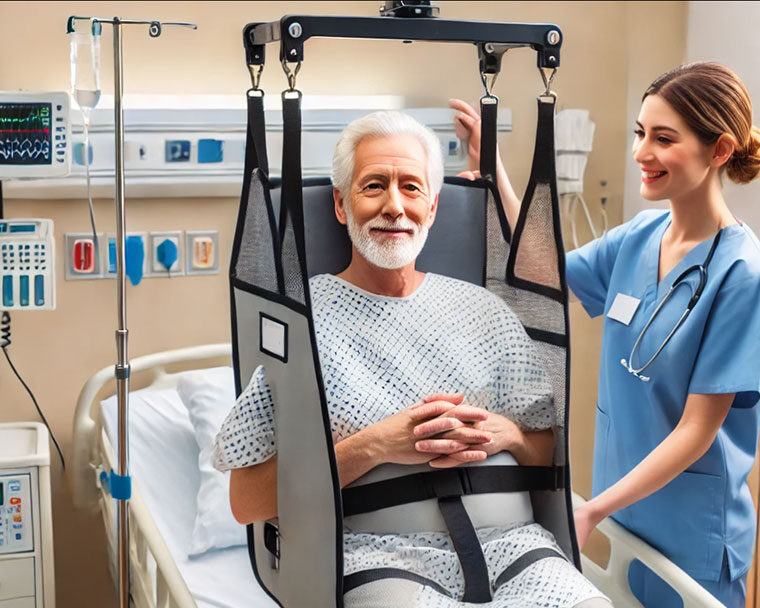
Preventing Caregiver Injuries: The Hidden Risks of Lifting and Caring for Patients
Caregivers play an essential role in the healthcare system providing invaluable support and assistance to patients with various medical conditions, disabilities or age-related limitations. Their responsibilities range from helping patients with daily activities such as bathing, dressing and feeding, to performing complex medical tasks such as administering medication and monitoring vital signs. In many cases caregivers must also lift, transfer or reposition patients to ensure their comfort and safety.
However, the physical demands of caregiving can pose significant risks to the caregivers themselves. Injuries resulting from lifting and caring for patients are a serious concern that must be addressed to protect the well-being of those who dedicate their lives to helping others. This article aims to shed light on the hidden risks of lifting and caring for patients, focusing on the prevalence of caregiver injuries, common causes and effective prevention strategies. By raising awareness and implementing best practices, caregivers, healthcare organizations and policymakers can work together to create a safer environment for all.
The Burden of Caregiver Injuries
Caregiver injuries are a prevalent issue in the healthcare sector affecting a significant number of professionals and family caregivers alike. According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, healthcare workers experience some of the highest rates of non-fatal occupational injuries and illnesses. Nursing assistants, in particular, are among the most at risk for musculoskeletal injuries due to the frequent lifting and moving of patients. Family caregivers, who often lack formal training, are also susceptible to injuries as they navigate the physical demands of caregiving.
Injuries sustained by caregivers can have far-reaching consequences on their mental and physical well-being. Physical injuries such as strains, sprains and back problems can result in chronic pain, limited mobility and reduced quality of life. Additionally, the psychological toll of sustaining an injury can lead to increased stress, anxiety and depression. In some cases, the fear of reinjury may cause caregivers to be overly cautious or hesitant in their duties, potentially compromising the quality of care they provide to patients.
The economic impact of caregiver injuries is substantial. Injured caregivers may require costly medical treatment, rehabilitation services and time off work to recover. These expenses can place a financial burden on the individual, their family and the healthcare system as a whole. Moreover, high rates of caregiver injuries can lead to increased employee turnover, absenteeism and decreased productivity further exacerbating the financial strain on healthcare organizations.
Common Caregiver Injuries and Their Causes
Musculoskeletal injuries are among the most common types of injuries sustained by caregivers, often resulting from the physical demands of lifting, transferring and repositioning patients. Strains and sprains frequently occur when caregivers overstretch or use improper techniques while assisting patients. Back injuries such as herniated discs and muscle strains can be particularly debilitating and may result from repeated lifting or poor body mechanics.
Repetitive stress injuries are another common issue faced by caregivers. These injuries develop over time due to the repeated performance of certain tasks or movements such as bending, twisting or reaching. Carpal tunnel syndrome, tendonitis and bursitis are examples of repetitive stress injuries that can affect caregivers.
Several factors contribute to the occurrence of caregiver injuries. Poor lifting techniques such as bending at the waist or twisting while lifting can place excessive strain on the muscles and spine, increasing the risk of injury. Overexertion, whether from lifting too much weight or working for extended periods without breaks, can also lead to injuries. Additionally, a lack of training and education in proper caregiving techniques can leave caregivers ill-equipped to safely perform their duties.
Recognizing the common causes of caregiver injuries is an essential step in developing effective prevention strategies. By addressing these factors, caregivers can reduce their risk of injury and maintain their ability to provide quality care to their patients.
Prevention Techniques and Best Practices
To minimize the risk of caregiver injuries it’s crucial to implement prevention techniques and adhere to best practices in lifting and caring for patients. These strategies can help protect caregivers from harm while ensuring that they can continue to provide quality care.
Proper body mechanics and lifting techniques are critical in preventing caregiver injuries. Adhering to the following guidelines for safe lifting can reduce the risk of strains, sprains and back injuries:
-
Keep a wide base of support by standing with feet shoulder-width apart.
-
Bend at the knees and hips, keeping the back straight and using leg muscles to lift.
-
Hold the patient close to the body to minimize the strain on the back and arms.
-
Avoid twisting while lifting; instead, pivot the feet to change direction.
-
Communicate and coordinate with the patient and other caregivers during lifting and transfers.
In addition to proper lifting techniques, using assistive devices can significantly decrease the risk of caregiver injuries. Equipment such as mechanical lifts, slide sheets and transfer boards can help facilitate safer patient handling and reduce the physical demands on caregivers.
Caregiver self-care is another essential aspect of injury prevention. Regular exercise and stretching can help maintain strength, flexibility and resilience which are crucial for avoiding injuries. Caregivers should also prioritize getting adequate rest and managing stress to maintain their overall well-being and reduce the risk of burnout.
Training and education programs play a vital role in preventing caregiver injuries. Continuous learning about best practices in patient handling and care can help caregivers stay up to date on the latest techniques and safety measures. Access to resources and support networks can also provide valuable guidance and encouragement for caregivers striving to maintain their health and safety while caring for others.
Role of Healthcare Organizations and Employers
Healthcare organizations and employers have a crucial role to play in preventing caregiver injuries and promoting a safe working environment. By implementing the following strategies, they can help ensure the well-being of their caregivers and ultimately contribute to better patient care:
Providing necessary equipment and resources:
Healthcare organizations should invest in assistive devices and other equipment that can facilitate safer patient handling. Regular maintenance and replacement of equipment, as needed, can help ensure that caregivers always have access to functioning and up-to-date tools for their tasks.
Implementing and enforcing safety protocols:
Employers must establish clear safety protocols and guidelines for lifting and caring for patients taking into consideration the unique needs of their patient population. Regular training sessions and refresher courses can help ensure that caregivers remain knowledgeable about these protocols and understand their importance in preventing injuries.
Promoting a culture of safety and support:
Healthcare organizations should foster a workplace culture that prioritizes safety, encourages open communication and supports caregivers in their efforts to minimize injury risks. This may include creating a system for reporting safety concerns, recognizing and rewarding safe practices, and providing opportunities for caregivers to share their experiences and learn from one another.
By taking an active role in promoting caregiver safety, healthcare organizations and employers can help reduce the incidence of injuries and create a better working environment for those entrusted with the care of patients.
Legal and Regulatory Considerations
Complying with legal and regulatory requirements is essential for healthcare organizations and caregivers to ensure the safety of both patients and caregivers. Several guidelines and considerations must be taken into account:
Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) guidelines:
OSHA sets forth guidelines and standards for safe patient handling and movement, aiming to minimize the risk of injury to healthcare workers. These guidelines include recommendations for proper lifting techniques, the use of assistive devices and the implementation of safety protocols. Healthcare organizations and caregivers should familiarize themselves with these guidelines and make a concerted effort to comply with them.
Workers' compensation and caregiver injuries:
In the event of a caregiver injury, workers' compensation laws provide financial assistance for medical expenses and lost wages. Healthcare organizations must comply with these laws and caregivers should be aware of their rights and responsibilities under workers' compensation. Employers should have a clear process in place for caregivers to report injuries and seek the necessary support.
Reporting and recordkeeping requirements:
Healthcare organizations are typically required to maintain records of workplace injuries and report them to relevant authorities, such as OSHA or state workers' compensation boards. Accurate recordkeeping and reporting can help identify patterns of injuries and areas of concern ultimately contributing to the development of more effective prevention strategies.
By adhering to legal and regulatory requirements, healthcare organizations can help create a safer working environment for caregivers and demonstrate a commitment to their well-being.
Conclusion
Caregiver injuries, particularly those resulting from lifting and caring for patients, are a pressing concern that must be addressed to ensure the safety and well-being of those who dedicate their lives to helping others. By understanding the prevalence of these injuries and their underlying causes, caregivers, healthcare organizations and policymakers can work together to develop and implement effective prevention strategies.
Preventing caregiver injuries requires a multifaceted approach that encompasses proper lifting techniques, the use of assistive devices, self-care, training and education. Healthcare organizations and employers have a crucial role to play in providing the necessary resources, promoting a culture of safety and ensuring compliance with legal and regulatory requirements.
Ultimately, the responsibility for preventing caregiver injuries lies with everyone involved in the caregiving process. By prioritizing the well-being of caregivers and fostering a safe environment, we can help ensure that they can continue to provide quality care to their patients without compromising their own health and safety.
Discover QuickChange's innovative products designed to enhance patient care – explore our range of solutions today and invest in a safer, more efficient healthcare environment.
Further Reading
For those interested in delving deeper into caregiver injury prevention and safety, the following resources provide valuable information, guidance and best practices:
Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) – Safe Patient Handling: OSHA's comprehensive resource on safe patient handling covers guidelines, recommendations and strategies for reducing caregiver injuries in healthcare settings.
National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) – Safe Patient Handling and Mobility: NIOSH provides a wealth of research, guidelines, and resources on safe patient handling and mobility, focusing on both caregiver and patient safety.
American Nurses Association (ANA) – Safe Patient Handling and Mobility: ANA's Safe Patient Handling and Mobility initiative aims to educate nurses and healthcare organizations on best practices for preventing injuries while handling patients.
The Family Caregiver Alliance – Caregiver Health - The Family Caregiver Alliance offers resources, tips, and support for family caregivers, with a focus on maintaining their health and well-being while providing care.
These resources can help caregivers, healthcare organizations and policymakers develop a deeper understanding of the challenges associated with caregiver injuries and the steps that can be taken to create a safer and more supportive environment for all involved in patient care.

.webp?width=760&height=152&name=qc-banner%20(3).webp)

