Measuring Normal Urine Output: Practical Steps and Health Benefits
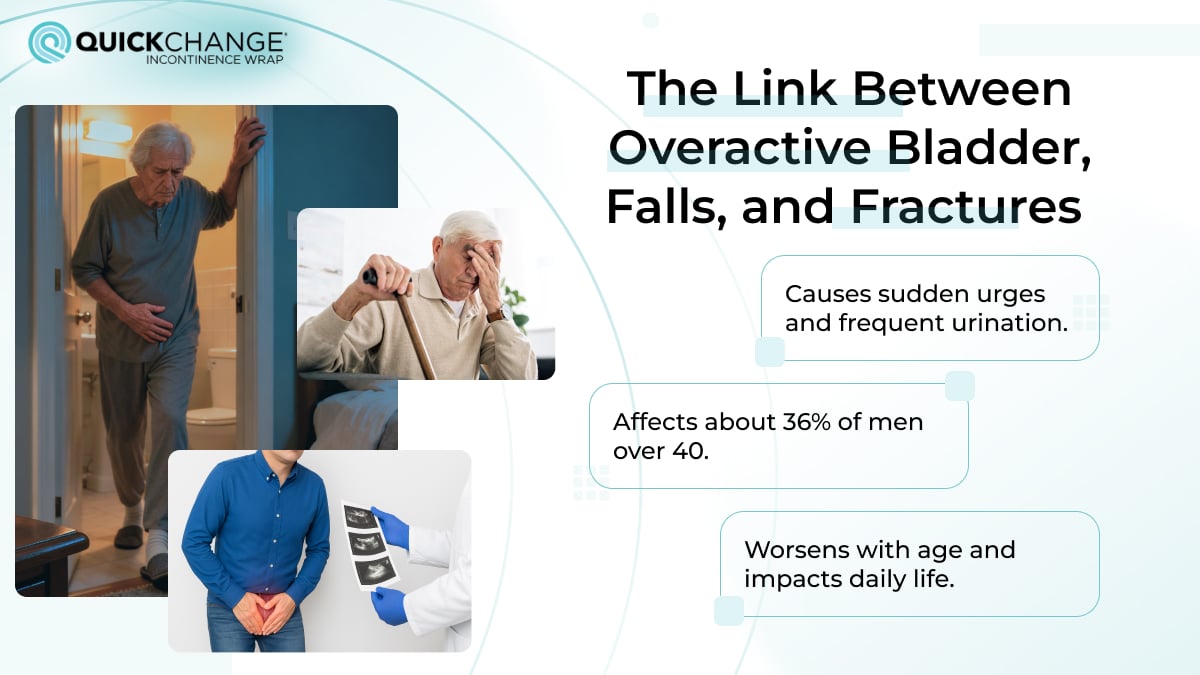
Most people rarely think about tracking their normal urine output in everyday life. However, for patients with limited mobility or those recovering from surgery, this process is quite important. Even minor changes in urination can indicate to caregivers and medical staff that something is wrong with the body or kidneys, allowing serious complications to be prevented through timely detection.